[M1 Mac, Big Sur 11.6.5, Python 3.10.4]
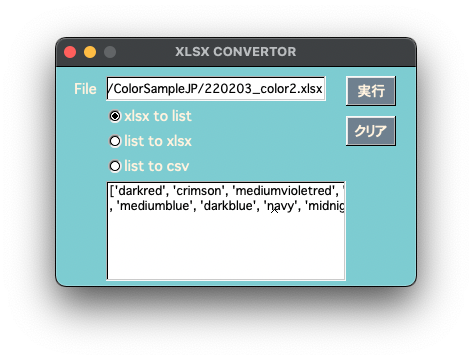
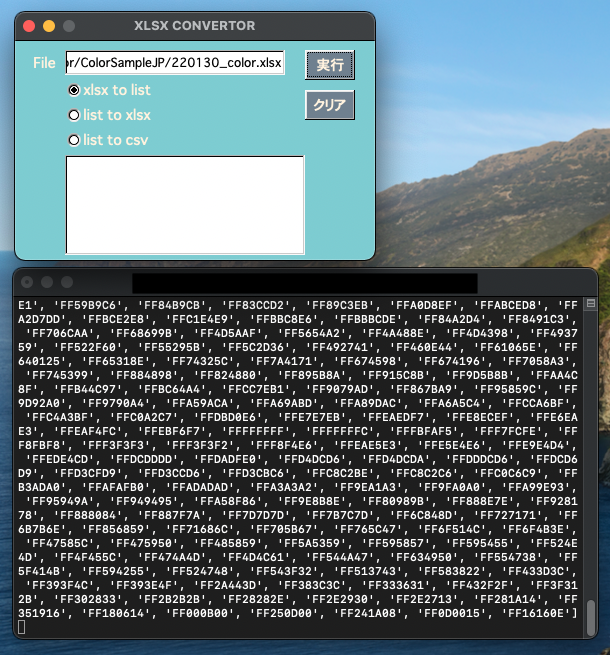
製作中のアプリですが、前回の記事でも書いたように実行ファイルでは正常に動作し、appファイルは起動はするもののボタンを押すと落ちてしまいます。
原因を探ったところ、どうやらPYTHONPATHを認識できないためにPyImport_ImportModuleが働かずモジュールが生成していないようでした。PYTHONPATHの__pycache__ディレクトリにpycファイルが生成していないことで判明しました。
appファイル内の/Contents/Resourcesにpyファイルを置き、info.plistで認識させようとするなどいろいろ試しましたが、うまくいきませんでした。
結局解決には至らず、やむなくこのまま次に進みます。Objective-Cであれば何らかの方法が見つかるかもしれません。
#define PY_SSIZE_T_CLEAN
#include "process.h"
#include </Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.10/include/python3.10/Python.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using std::string;
const char* XlsxToList(const char* path) {
Py_Initialize();
// sys.pathを確認 wchar_tなのでwcoutで出力
std::wcout << Py_GetPath() << std::endl;
// pyファイルのモジュール化 appファイルではモジュール化できない PYTHONPATHに到達できていない
PyObject* myModule = PyImport_ImportModule("test");
// pyファイル内の関数を指定
PyObject* myFunction = PyObject_GetAttrString(myModule,(char*)"xlsx_to_list");
// 関数の引数を設定
PyObject* args = PyTuple_Pack(1,PyUnicode_FromString(path));
// 関数を実行し戻り値をPyObjectとして取得
PyObject* myResult = PyObject_CallObject(myFunction,args);
// PyObjectをconst char*に変換
const char* result = PyUnicode_AsUTF8(myResult);
std::cout << result << std::endl;
return result;
Py_FinalizeEx();
}